

Industry News
Gantry cranes are versatile and provide efficient lifting solutions for a wide range of industries. Furthermore, portable gantry cranes, in particular, offer enhanced flexibility, maneuverability, and convenience. As a result, they are ideally suited for a wide range of settings, such as construction sites, workshops, manufacturing plants, warehouses, and shipyards.
In this comprehensive guide, we will clearly outline how to build a gantry crane, thereby helping you understand both its fundamental concepts and the key steps required for its construction.
Gantry cranes are designed based on bridge cranes and feature a unique portal frame structure consisting of a horizontal main beam, rigid outriggers, and a running mechanism. They are primarily used for handling and installation operations in open-air storage yards, shipyards, power stations, ports, and railway freight stations.

Building a gantry crane is a complex engineering project that requires comprehensive consideration of design, material selection, manufacturing, and installation. Then the following are the main steps in building a gantry crane:
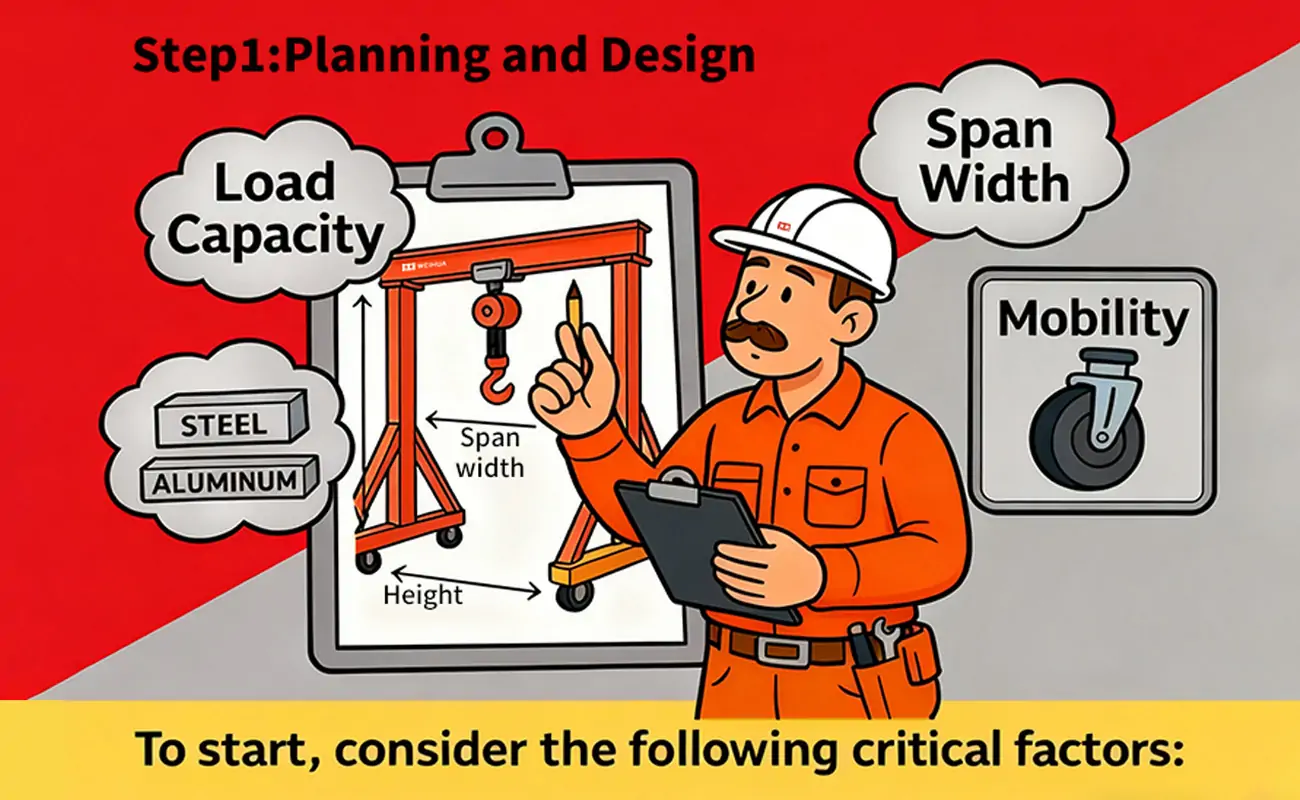
Before beginning construction, consider these key factors:
- Load Capacity: Determine the maximum weight the gantry crane will need to lift.
- Span Width: Measure your workspace to determine the length of the crane beam.
- Height: Determine the height clearance required for operation.
- Mobility: Choose between fixed, track-mounted, or mobile (with rubber tires).
- Material: Steel or aluminum are common choices.Steel effectively handles larger loads, whereas aluminum excels in providing lightweight portability.
- Mobility: Choose between fixed placement and mobile.
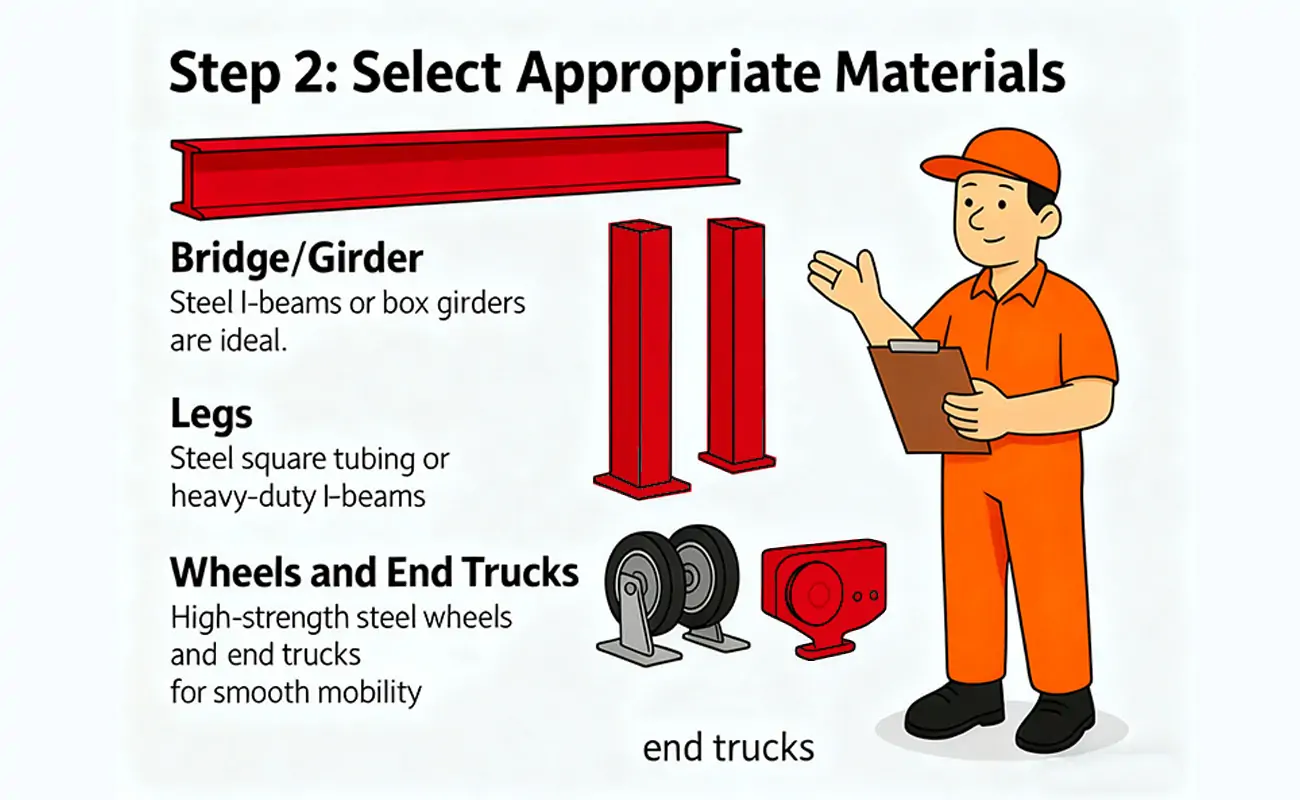
High-quality materials are crucial to the structural integrity of a gantry crane.
- Bridge/Girder: Typically made of steel or aluminum, it supports the crane's load. Steel I-beams or box girders are ideal.
- Outriggers: Vertical structures that firmly support the crossbeam. They can be made of steel square tubes or heavy-duty I-beams.
- Wheels and End Forks: High-strength steel wheels and end forks ensure smooth movement.
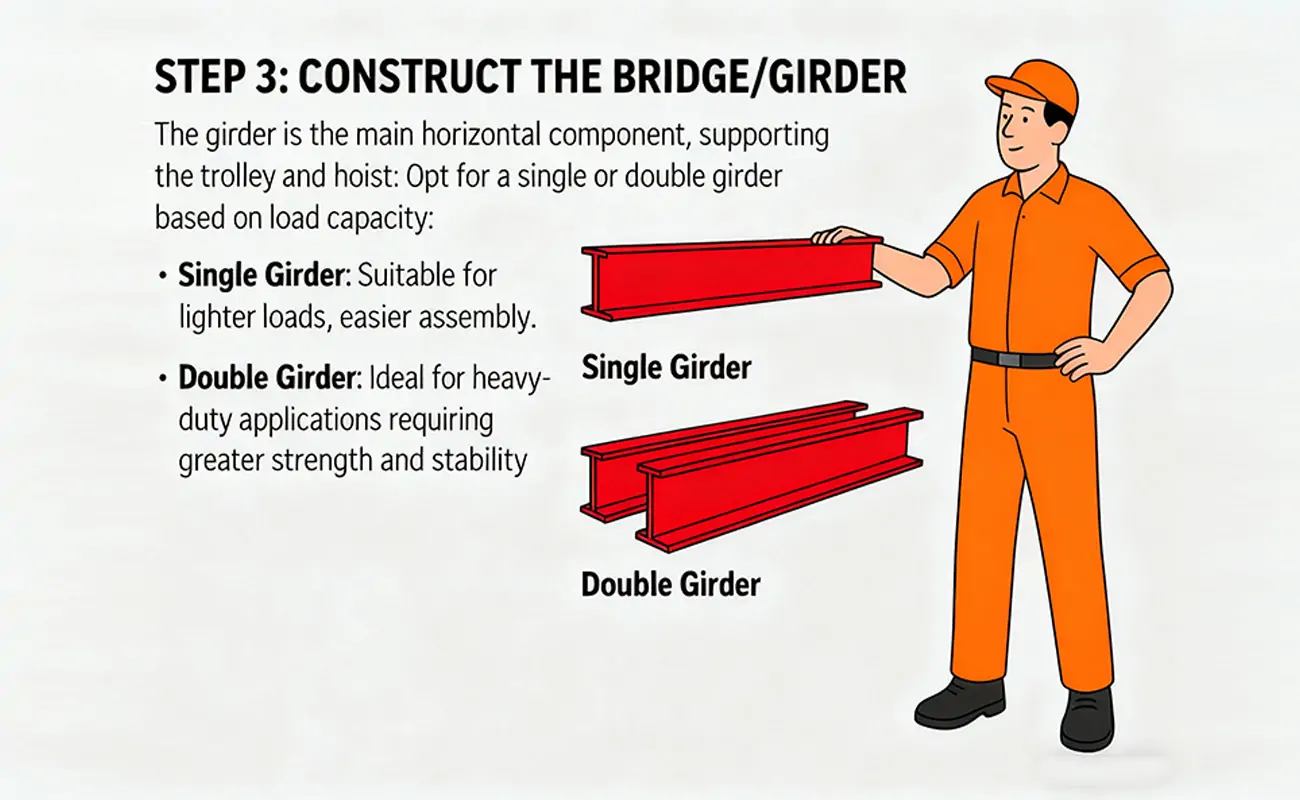
The main beam serves as the primary horizontal component, directly supporting the trolley and hoist. Therefore, when making your selection, be sure to choose between a single or double beam design based on your required load capacity.
- Single beam: Suitable for lighter loads and easier assembly.
- Double beam: Suitable for heavier loads requiring greater strength and stability.
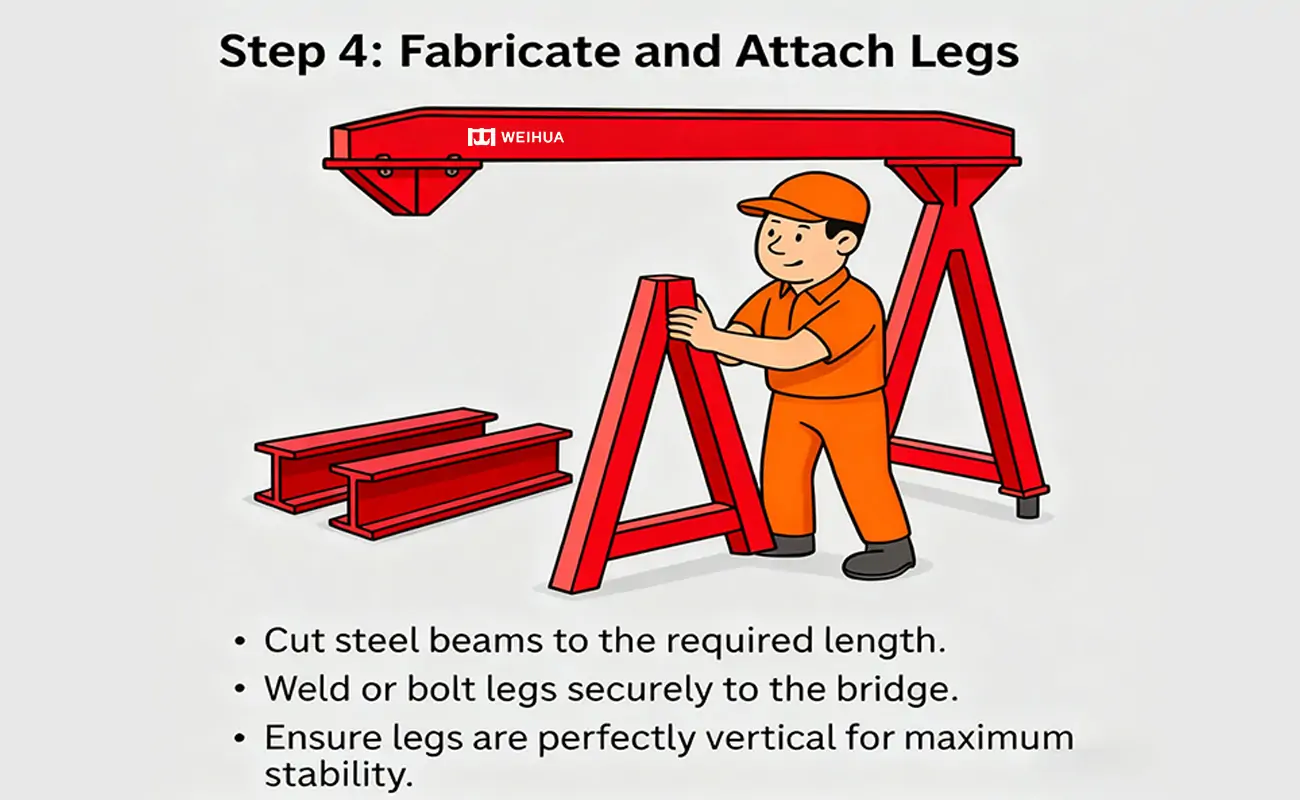
The outriggers support the bridge and must be strong enough to withstand the operating loads:
- Cut the steel beams to the required lengths.
- Securely weld or bolt the outriggers to the bridge.
- Ensure the outriggers are perfectly vertical for maximum stability.
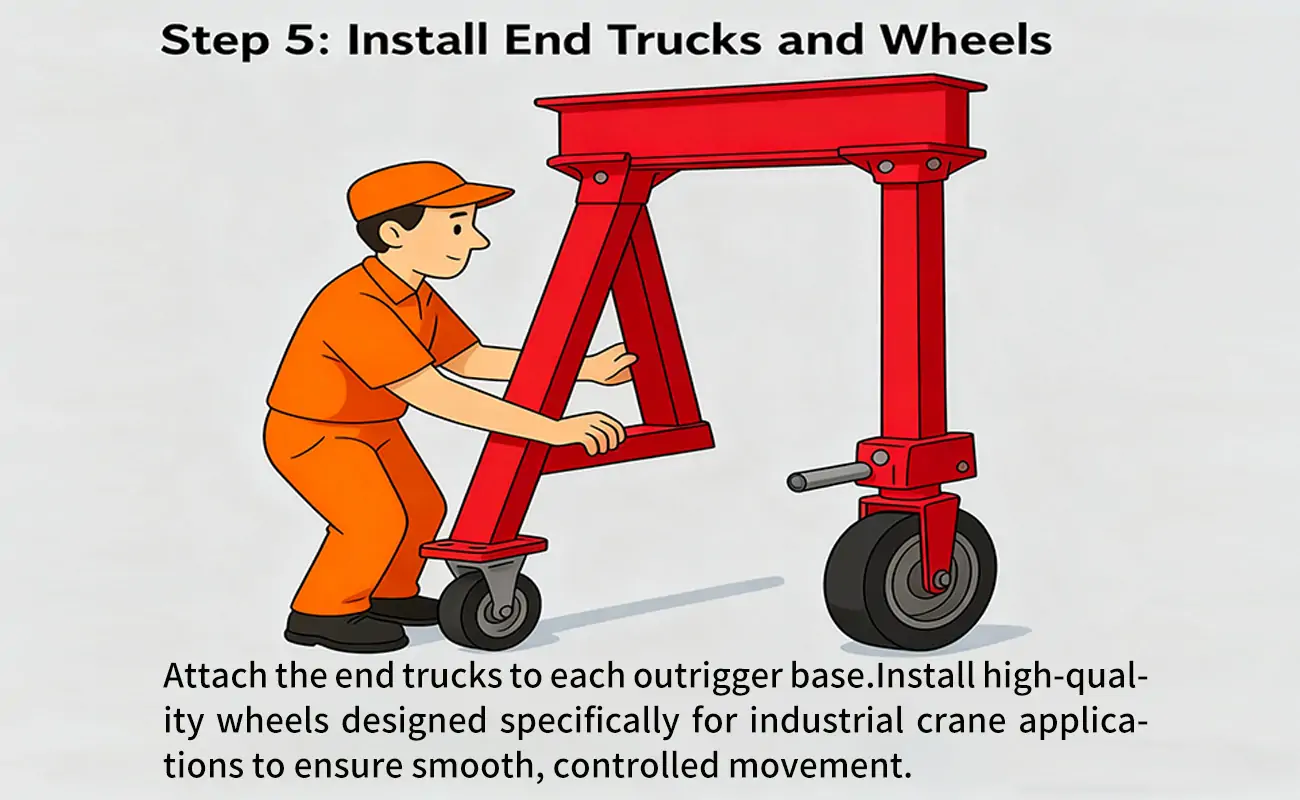
End trucks support crane movement:
- Securely attach the end trucks to each outrigger base.
- To ensure smooth and controlled movement, it is essential to install high-quality wheels that are designed specifically for industrial crane applications.
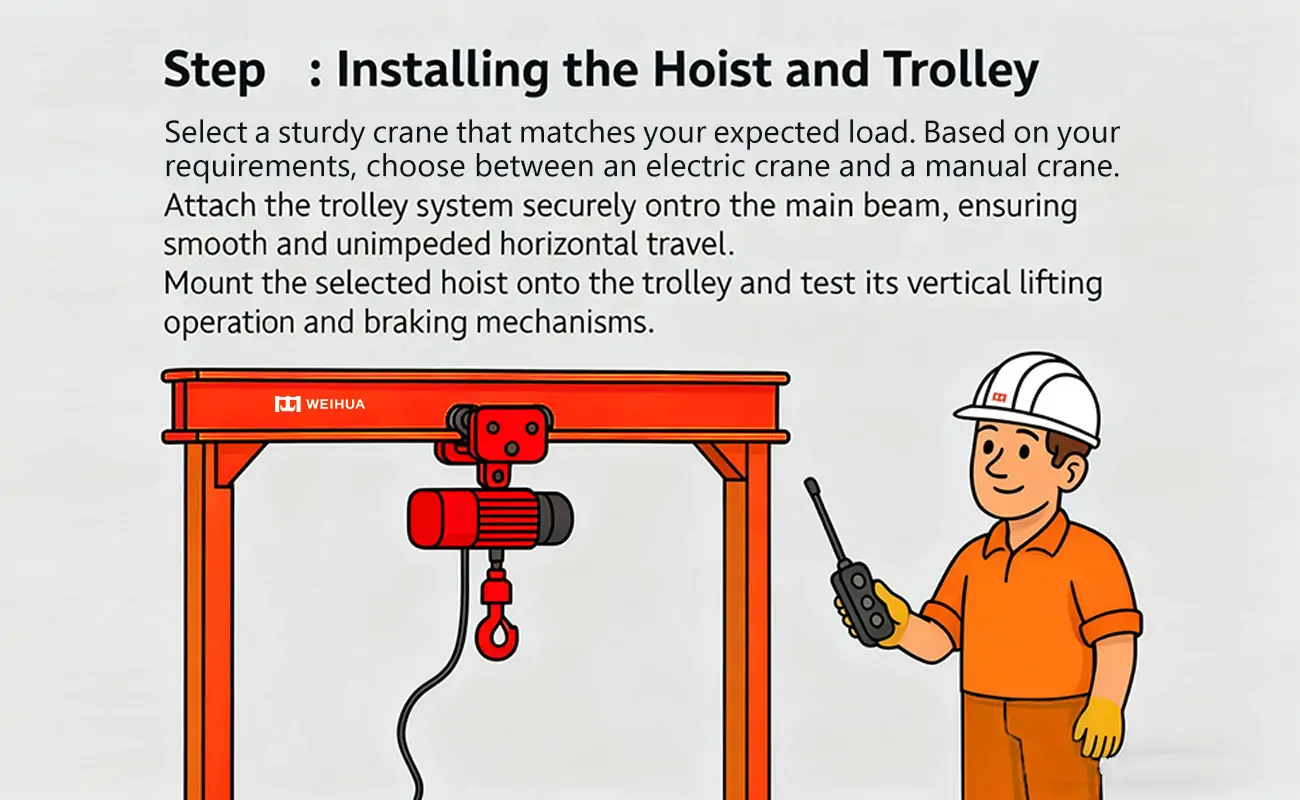
To ensure safe and efficient operation, select a robust hoist compatible with your intended load; additionally, choose between an electric or manual model based on your specific operational needs.
Securely mount the trolley system to the main beam, ensuring smooth and unobstructed horizontal movement.
Attach the selected hoist to the trolley and test its vertical lift operation and braking mechanism.
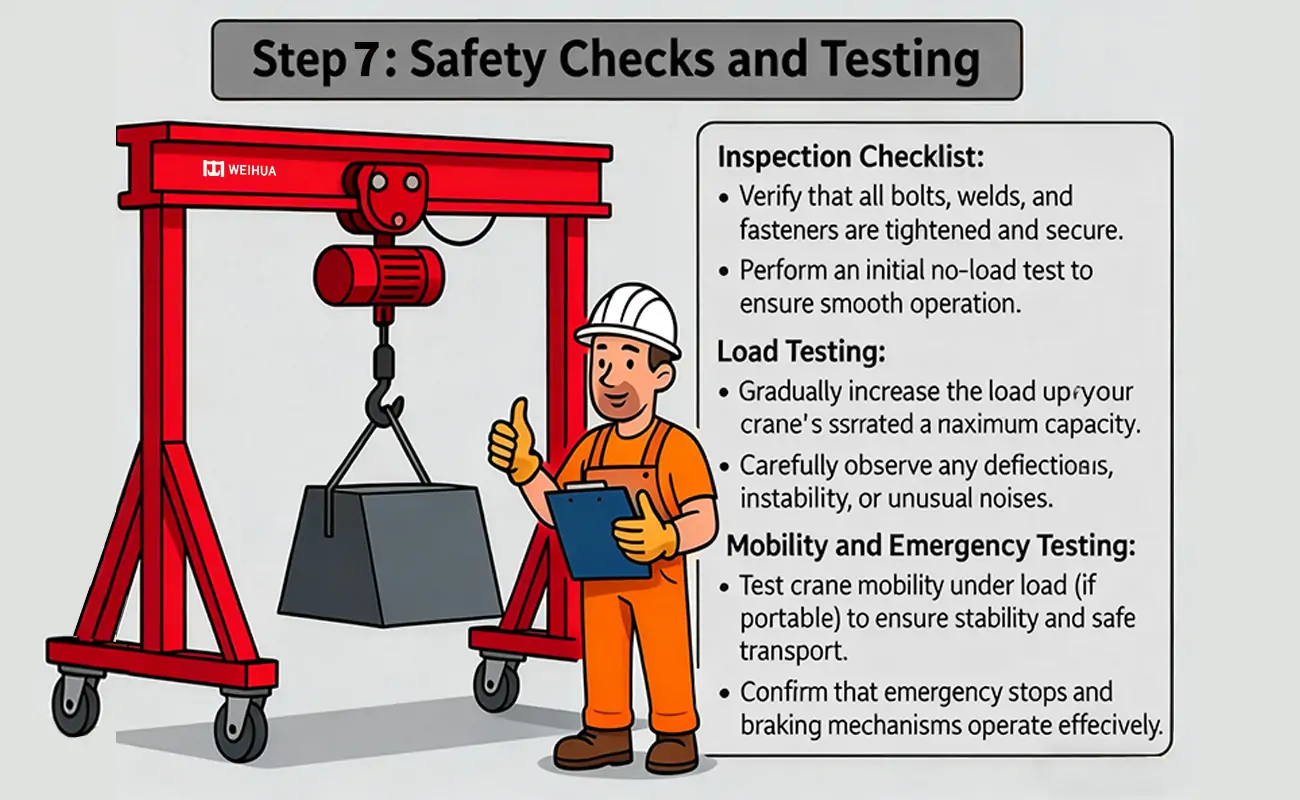
Checklist:
Confirm that all bolts, welds, and fasteners are tightened and secure.
Perform an initial no-load test to ensure smooth operation.
Load Test:
Gradually increase the load until the crane's rated maximum capacity is reached. Carefully observe for any deflection, instability, or unusual noises.
Mobility and Emergency Test:
Test the crane's mobility under load (if portable) to ensure stability and safe transport.
Confirm that the emergency stop and braking mechanisms operate effectively.
Throughout the entire process—from selecting the crane type and structural materials to choosing the main girder, hoisting mechanism, pulleys, and travel wheels—engineers must make a series of interconnected decisions, which together form a complete and functional equipment system.As a result, they design the gantry crane to achieve a stable structure and reliable performance, ensuring it meets long-term operational demands.
For customized gantry crane solutions, please feel free to contact us. Our professional team will provide you with personalized advice and help you choose the most suitable equipment.
Submit Request