

Noticias
Jib cranes are an essential lifting solution for a wide range of industries, primarily used for precise, repetitive material handling in localized workspaces. How Does a Crane Jib Work depends largely on the type of construction and how it is mounted. Jib cranes can be mounted on floors, walls, and mobile bases. Jib cranes utilize a jib (or boom) to support and efficiently move loads within a specific radius.
In this article, we will take you through the working principle, main components, application scenarios, different types, advantages, and disadvantages of jib cranes. Read on for a comprehensive look at jib cranes and how they can improve lifting efficiency.

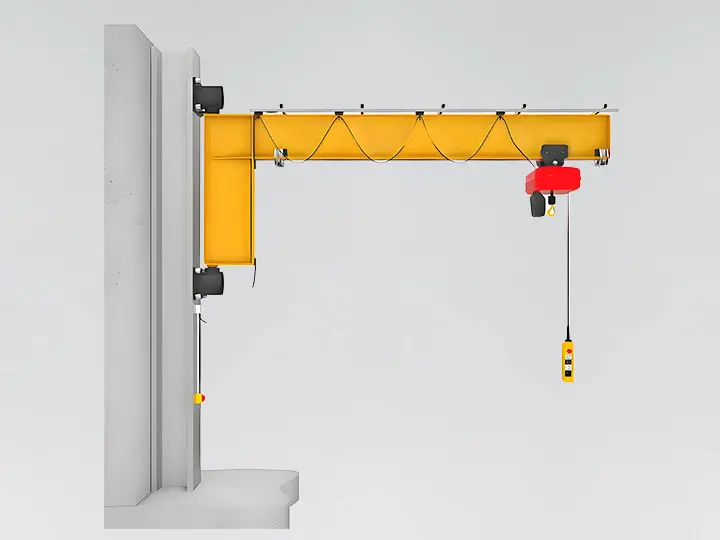
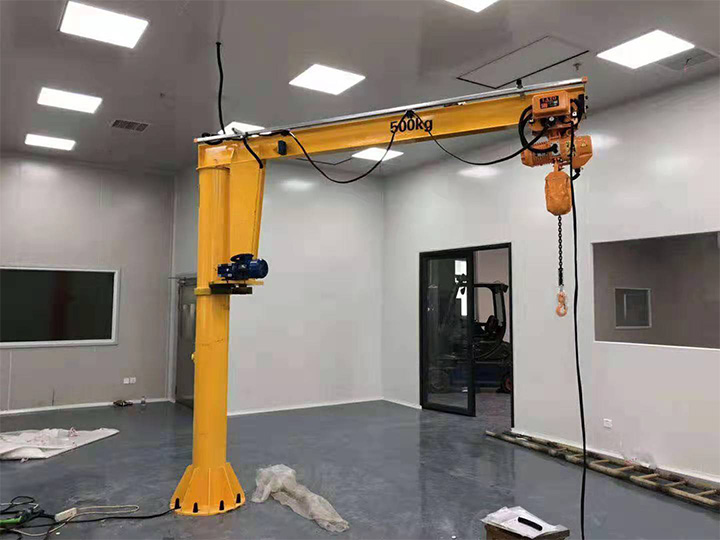
The working principle of a jib crane is simple; at its core, it is based on a horizontal arm (also known as a jib or boom) that is attached to a vertical support, either a column mounted on the floor or a bracket on the wall. The lift moves horizontally along the cantilever, lifting and transporting loads within a circular or semi-circular working area. The cantilever has a swivel range of 180° to 360°, allowing flexible handling of loads in localized areas. Depending on the system design and workload requirements, lifting and moving operations can be either manual or motorized.
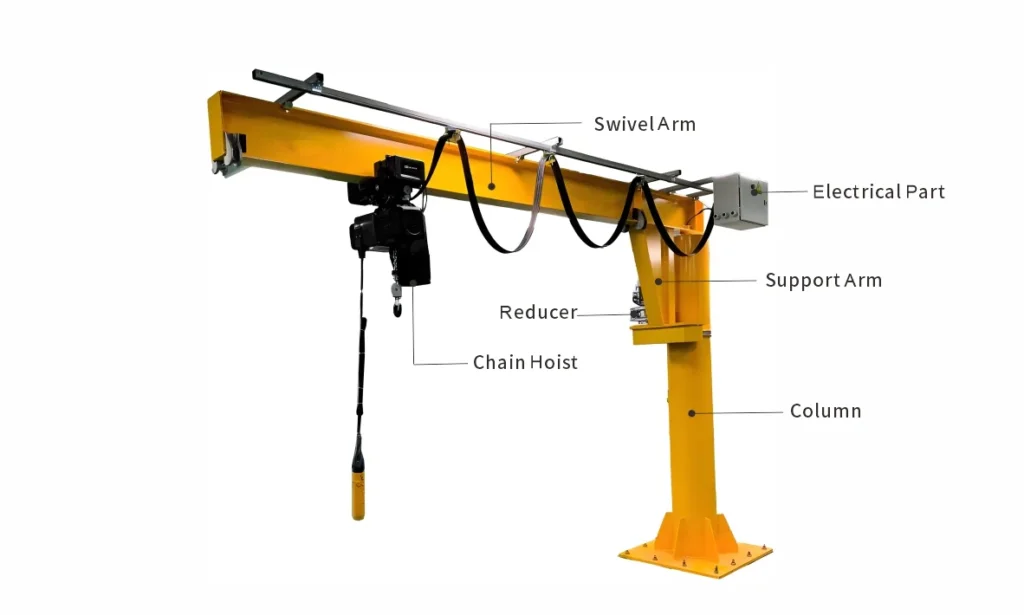
Jib (Boom): Horizontal beam that supports the crane and allows it to move laterally. It determines the reach and working area of the crane.
Column or Mounting Bracket: Vertical column (optional freestanding or floor-mounted) or wall bracket (wall-mounted) that supports the jib and allows it to rotate.
Lift: A lifting device mounted on a trolley that moves along the cantilever. Electric, manual, or pneumatic options are available.
Trolley: A Mechanical device that moves the electric hoist horizontally along the cantilever for smooth operation.
Slewing mechanism: Rotates the cantilever 180°~360°. Depending on the load capacity and frequency of operation, it can be manual or electric.
Base plate or wall bracket: Provides structural support and anchoring to ensure safe operation.
Electrical control system: Includes pushbutton station or remote control for operation of the lifting and rotating mechanisms.
There are several types of jib cranes, including column, wall-mounted, and folding jib. Here are a few common types, features, and applications:
| Tipo | Mounting | Capacidad de elevación | Rotation Angle | Key Features | Aplicación |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freestanding Jib Crane | Floor-mounted with foundation | Up to 5 tons | 360° | Independent structure; ideal for open workspaces | Loading bays, workshops |
| Wall-Mounted Jib Crane | Mounted to the wall and moves along a rail | Up to 2 tons | 180° | Space-saving; no floor obstruction | Assembly lines, fabrication areas |
| Wall-Traveling Jib Crane | Mounted to wall and moves along a rail | Up to 1 ton | Horizontal travel | Covers linear zones along walls | Production lines |
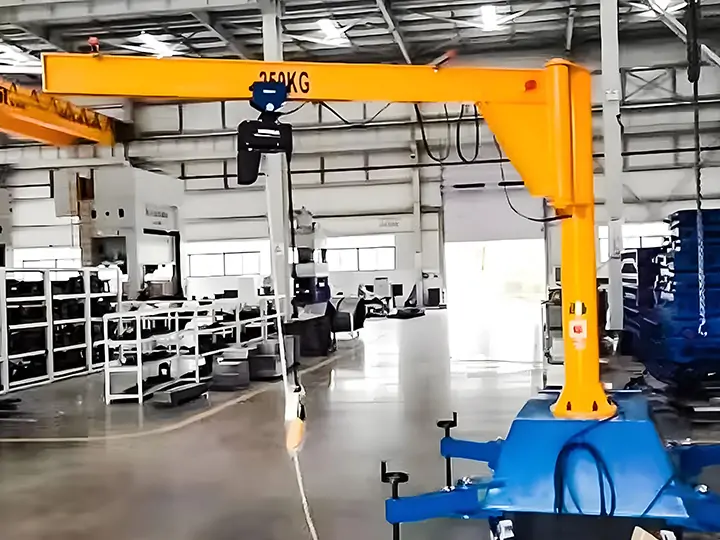
| Mobile Jib Crane | Wheeled or base-mounted | Typically up to 0.5 ton | Varies | Portable and flexible | Light-duty lifting, small workshops |
| Articulating Jib Crane | Floor or wall-mounted | 150–500 kg | Multiple joints | Multi-axis movement | Mounted to the wall or column |
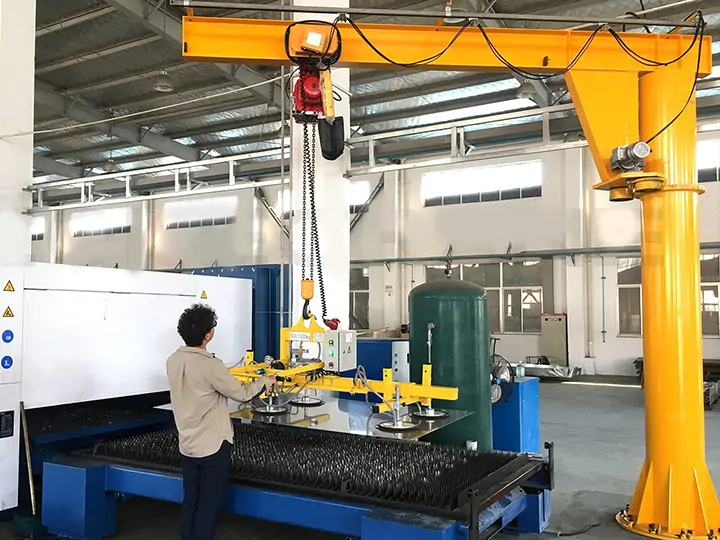
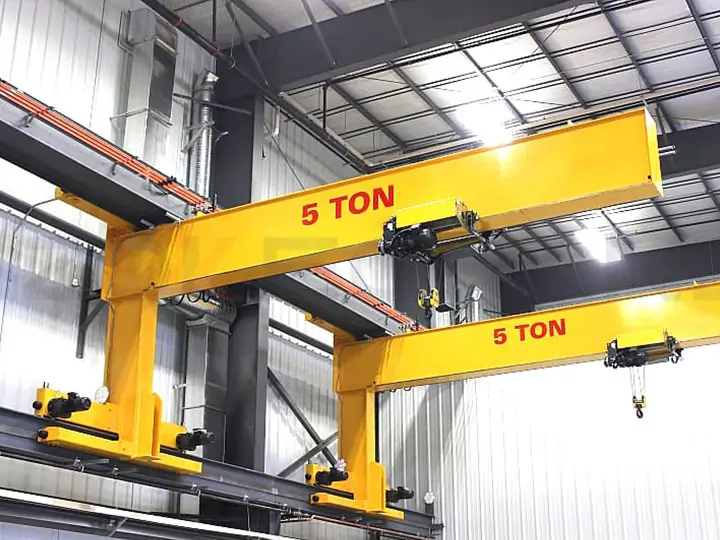






Manufacturing plants: For moving components between workstations or machines.
Warehouses: Assisting in loading/unloading goods from vehicles or storage areas.
Assembly lines: Supporting precise and repetitive lifting in tight areas.
Shipyards: Handling tools, parts, or equipment during vessel assembly.
Metalworking and machining shops: Assisting operators in handling heavy molds or fabricated parts.
Logistics and distribution centers: Streamlining order fulfillment and package handling.
We suggest you to choose the right type of jib crane depends on workspace layout, load handling needs, and desired automation level.
Operating a jib crane involves the following steps:
Inspect before use: Check for visible damage or wear on hoist, trolley, and structure.
Power on the system: Ensure the crane is connected to its electrical source if motorized.
Position the jib arm: Rotate the jib arm manually or via motor to align with the load.
Lift the load: Use the hoist control panel to raise the load safely.
Move horizontally: Slide or drive the trolley along the jib to position the load.
Lower the load: Carefully lower the load at the destination point.
Return the arm: Move the jib back to the starting position after use.
Power off and secure: Turn off the system and conduct any necessary post-operation checks.
Never exceed rated load capacity.
Avoid sudden movements or swinging loads.
Keep the area below the load clear of personnel.
Weihua Group is a leading manufacturer and supplier of jib cranes with over 30 years of industry experience. We specialize in custom-designing jib cranes for your specific application, whether it's a freestanding 360° swivel system for outdoor use or a compact wall-mounted crane for use in tight factory spaces. Contact us today for a personalized jib crane solution for your plant.
Jib cranes offer a practical, efficient, and cost-effective way to handle materials in localized work zones. By understanding how a crane jib works, what its components are, and how to choose the right type, you can greatly improve the efficiency and safety of your operations.
If you have any questions or need help selecting the ideal jib crane for your facility, feel free to reach out to our experts at Weihua.
Enviar solicitud